{{item.title}}

The growth of internet of things (IoT) and connected devices across industries has resulted in unparalleled volumes of data, the scale and complexity of which have outpaced network and infrastructure capabilities. Transferring all that device-generated data to a centralised data centre or the cloud causes bandwidth and latency issues. Edge computing with 5G aims to solve this issue. Edge computing refers to the concept of a distributed system that brings data storage and computations closer to the sources such as IoT devices. This eliminates the need for centralised data storage and processing systems, as a result of which real-time data application performance is not affected by latency issues.
Edge computing paves a better way for industries and businesses in optimising real-time data analysis. With the number of IoT connected devices expected to reach 43 billion by 2023, edge technology can help process the copious amounts of data that this surge in IoT-enabled devices will produce, ushering in the next industrial revolution by transforming business processes to make them faster and more agile. The global edge computing market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 19% from USD 36.5 billion in 2021 to USD 87.3 billion by 2026.
The factors driving edge computing are lower latency, bigger bandwidth, improved security and better computing capacity.
Edge computing is an evolution of the cloud model and its benefits depend on the sensitivity of business use cases. For example, edge computing could reduce delays in use cases where the reaction time of devices/IoT is critical and sending data to and from the cloud or a data centre could cause slowdowns.
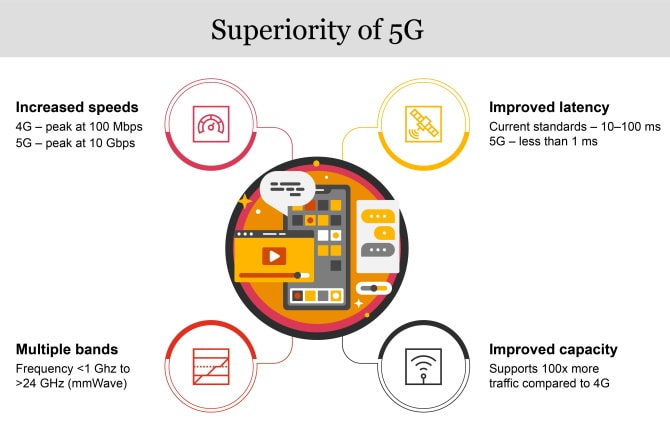
While 4G networks provided a maximum speed of 100–200 Mbps, 5G peak speeds are expected to be around 10 Gbps – a hundred-fold increase in speed. 5G accomplishes this task by utilising a wide array of the spectrum from lower bands (frequency <1 GHz) to higher bands called millimetre wave (mmWave; frequency >24 GHz). The capacity of these mmWave frequencies is many times higher than that of existing technology, hence improving the efficiency of 5G.
5G tech has also seen communication of very minimal latency (<1 millisecond). This would mean that there would be no significant delay times associated with the network, making it much more reliable and enabling seamless real-time access to technology.
5G technology has a few unique characteristics which are part of the 5G New Radio (NR) standards, set up by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project).
eMBB is one of the use cases whereby 5G will be able to deliver its full potential to the masses. Through eMBB, 5G will be able to provide gigabits of data speed through mobile broadband. A real ‘hotspot’ situation could be where hundreds and thousands of fans are utilising limited broadband and connectivity during a sports event or a concert, and eMBB could deliver the required speeds to provide connectivity to the crowd.
Quicker response time has been an ask with each evolution of cellular technology, and 5G will be able to meet this demand in a remarkable way. Latency has been a barrier for technologies dependent on processing huge amounts of data with near to no delay. Through urLLC, 5G will empower technology to do just that. Thanks to 5G, technology like self-driven vehicles or augmented reality (AR) supported surgery will become possible in the near future.
mMMTC is the 5G use case focusing on a large number of IoT-connected systems. It could help in large-scale deployment of machines that perform simple functions and have low power utilisation.
5G is ushering in development and revenue in industries across the world. A recent analysis shows that by 2035, 5G technology will transform industries worldwide, generating output worth USD 13.2 trillion globally and creating job opportunities for more than 22 million people.5
5G is also impacting areas like IoT, virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI) due to its improved connectivity, speeds, reliability and low latency. It is opening new avenues and experiences such as instant access to cloud services, real-time collaboration, medical consultation and low-latency cloud gaming.
1. Enhanced speed
As a result of having compute power at the edge, the need for data to travel to the centralised data centres is reduced. This saves time and helps in faster real-time decision making needed for any potential uses in businesses.
2. Improved reliability
The edge computing technology provides better reliability to critical systems as the latency is low and real-time decisions are made faster. Thus, any application will not halt or buffer due to speed issues.
3. Better data management
Edge computing moves some of the data computation and processing requirements near the edge points, thereby reducing the need to send all the data to centralised data centres. Thus, edge computing topology helps in the better management of data.
Optimising real-time data in retail.
As more and more retail stores and e-commerce warehouses start to adopt digitalisation, edge computing is gaining an increased importance in this space. It helps to locally process information and facilitate real-time decision making based on the real-time data collected from each warehouse. This helps to optimise and speed up the process of inventory management in warehouses.
Edge computing can be used to monitor and track the micro location of each inventory box in warehouses. This application helps to increase the efficiency of warehouse operations which is all about the accuracy and speed of storage and dispatch. The edge computing technology is integrated with smart cameras and the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system of the warehouse for this function. The smart camera present in that location of the warehouse reads the barcode tags on the inventory boxes that are stored in the same location.. This metadata is then sent to edge points where it is analysed in real time and the location information is passed on to the warehouse ERP for storage. In case the boxes are misplaced or moved to different locations in the warehouse, the smart camera can capture that data which is analysed by the edge point. The warehouse management is then alerted about the discrepancies observed.
In the manufacturing industry, edge computing can help to increase margins and operational efficiency. Edge computing helps data to be analysed faster so any equipment or process anomalies can be identified earlier to avoid shutdowns.
In the oil and gas industry, reports on pipeline and equipment maintenance take weeks to analyse manually. Thanks to edge computing technology along with machine learning (ML) analytics, organisations in this industry are able to proactively carry out predictive maintenance, thus preventing failures that have huge environmental and financial costs.
Security systems transmit a huge amount of data to the cloud. Edge computing helps security systems to become smarter and faster as it eliminates the need for bulk data transfer and instead transfers data only when needed.
In the case of a surveillance camera installed in an important place like a bank where the video is recorded 24x7, it takes a long time if the bulk data has to travel to a centralised server for inferencing. To get a dynamic response, AI can do faster inferencing with the help of edge computing technology that is used to store that data near the camera source.
Edge computing plays a significant role in the healthcare industry. Medical equipment and devices collecting data frequently require faster decision-making capabilities to cater to patients. Edge computing helps in real-time health or fitness-related decision making based on the data collected from fitness equipment and critical care equipment.
Patients arriving in hospitals during emergencies can be diagnosed accurately during transportation so that hospitals can start treating the patients as soon as they reach. Edge computing can help in real-time analysis of patient data like vitals from sensors and monitors. The mobility, low latency and data processing capabilities of edge computing help in the real-time diagnosis of the patient, based on which paramedics can properly treat patients on their way to hospitals. This application of edge computing can avoid treatment-related delays that can effectively save lives of critical patients.
Edge computing can increase the potential of 5G technology. For data-intensive applications, even the speed of 5G technology wouldn’t be able to provide a smooth customer experience with data being transferred to the cloud for computing. Edge computing helps to provide localised data processing capabilities for these applications and gives customers a better experience while enjoying edge computing with 5G speed.
Augmented reality, IoT, and robotics applications coupled with the power of edge computing can deliver better performances. It also helps in reducing data centre footprints for these applications.
As edge computing keeps developing, upcoming businesses will experience and utilise technologically advanced and innovative solutions that will help them run their organisations more efficiently. Edge computing helps the Industrial Revolution 4.0 to reach its next stage through smart solution and process advancements.